Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
The dermal tissue of a plant provides ____ for the plant.
A) | support | C) | protection | B) | water
| D) | oxygen |
|
|
|
2
|
Adam visits Redwood National Park and learns that redwood trees grow to heights
of more than 100 m. How do trees get water and nutrients from the soil to their tops?
A) | Transpiration from the leaves pulls water upward. | C) | Xylem contract and push water and
nutrients upward | B) | Gravity continually pulls water and nutrients upward | D) | Trees use energy from ATP to push water and
nutrients upward. |
|
|
|
3
|
In higher plants, water flows through a system of lignified tubes called
______.
A) | xylem | C) | companion cells | B) | phloem | D) | stomata |
|
|
|
4
|
Lamila wants to determine the rate at which a plant uses water. She fills a
beaker with 80 mL of water and places a leafy flower stem into the beaker through a small opening in
the beaker's cap. Lamila then places the beaker near a sunny window. One week later, 47 mL of
water remains in the beaker.What plant process best explains the loss of water in the beaker?
A) | Germination | C) | Respiration | B) | Photosynthesis | D) | Transpiration |
|
|
|
5
|
The photosynthetic tissue of the leaf is called __________.
A) | mesophyll | C) | cuticle | B) | cortex
| D) | epidermis |
|
|
|
6
|
After fertilization, this part of a plant eventually becomes the fruit.
A) | Seed | C) | Sepal | B) | Ovary | D) | Petal |
|
|
|
7
|
The evaporation of water from leaves is called __________.
A) | turgor pressure | C) | osmosis | B) | transpiration | D) | wilting |
|
|
|
8
|
_____ from the male plant must land on the _______ of the female plant in a
process called _______.
A) | Pollen, stigma, pollination | C) | Pollen, anther,
pollination | B) | Pollen, stigma, fertilization | D) | Pollen, ovary,
pollination |
|
|
|
9
|
The part of a flowering plant that contains pollen is called the:
A) | Filament | C) | Style | B) | Stigma | D) | Anther |
|
|
|
10
|
Which structure is considered the male reproductive part of a flowering
plant?
A) | Stamen | C) | Carpel | B) | Petal | D) | Sepal |
|
|
|
11
|
Water flows through plants in the following sequence:
a) transpiration from
the leaves
b) absorption from the soil by root hairs
c) movement from roots to stem
d)
flow upwards in the stem
A) | b,c,d,a | C) | c,d,b,a | B) | a,b,c,d | D) | c,a,b,d |
|
|
|
12
|
Flowers that contain both stamens and carpels are called:
A) | Complete flowers | C) | Perfect flowers | B) | Total flowers | D) | Imperfect
flowers |
|
|
|
13
|
The purpose of phloem in plants is to _________.
A) | transport water and minerals | C) | enable the plant to
grow | B) | transport sugar and organic compounds | D) | produce a tough covering for plant stems
|
|
|
|
14
|
The leaf-like structure that protects the budding flower is called the:
A) | Petal | C) | Anther | B) | Sepal | D) | Style |
|
|
|
15
|
When water enters guard cells, the stomata _________.
A) | open | C) | do not change | B) | cannot carry on gas exchange
| D) | close |
|
|
|
16
|
Flowering plants are also called:
A) | Ferns | C) | Gymnosperms | B) | Angiosperms | D) | Mosses |
|
|
|
17
|
Hummingbirds transfer pollen from one flower to another while feeding. What
plant structure contains the pollen?
A) | Carpel | C) | Sepal | B) | Petal | D) | Stamen |
|
|
|
18
|
What are the three main parts of a seed?
A) | stored food, flower, and pollen grain | C) | cone, zygote, and seed coat
| B) | pollen grain, sperm, and egg | D) | seed coat, stored food, and an
embryo |
|
|
|
19
|
Photosynthesis occurs in plants in specialized organelles called ____.
A) | mitochondria | C) | lysosomes | B) | chloroplasts | D) | Golgi bodies |
|
|
|
20
|
Cotyledons
A) | abosorb sunlight. | C) | store nutrients. | B) | produce carbon dioxide. | D) | store water. |
|
|
|
21
|
The cotyledons in a seed
A) | protect the embryo. | B) | provide a source of food for the
embryo. | C) | develop from the seed coat. | D) | are part of the
gametophyte. |
|
|
|
22
|
Pines, spruces, and firs are
A) | angiosperms. | C) | flowering plants. | B) | gymnosperms. | D) | sometimes
nonvascular. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
23
|
The structure indicated at f
A) | supports the anther. | C) | supports the pistil. | B) | produces pollen. | D) | develops into a
fruit. |
|
|
|
24
|
The structure labeled c
A) | produces pollen. | B) | contains sperm cells. | C) | is the area where
pollen lands on and sticks. | D) | contains meristematic
tissue. |
|
|
|
The diagram below shows the stem of a coleus plant. 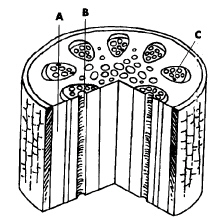
|
|
|
25
|
Refer to the illustration above. The tissue labeled A in the diagram is
called
A) | meristem. | C) | phloem. | B) | xylem. | D) | ground tissue. |
|
|
|
26
|
Refer to the illustration above. In the diagram, the tissue labeled B, which
conducts water and is made of elongated cells that connect end to end, is called
A) | meristem. | C) | phloem. | B) | xylem. | D) | ground tissue. |
|
|
|
27
|
Refer to the illustration above. In the diagram, the tissue labeled C, which
transports sugars from regions where they are made, to regions where they are used, is called
A) | meristem. | C) | phloem. | B) | xylem. | D) | ground tissue. |
|
|
|
28
|
The phloem in a plant
A) | transports sugars. | B) | transports water and
minerals. | C) | exchanges carbon dioxide and oxygen with the atmosphere. | D) | None of the
above |
|
|
|
The diagram below shows a leaf cross section. 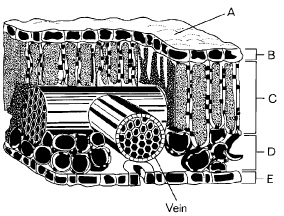
|
|
|
29
|
Refer to the illustration above. The vein illustrated is made up of
A) | only xylem vessels. | C) | both xylem and phloem vessels. | B) | only phloem
vessels. | D) | neither xylem nor
phloem vessels. |
|
|
|
30
|
Refer to the illustration above. The spongy layer is indicated at
|
|
|
31
|
Refer to the illustration above. Structure A
A) | is the cuticle. | C) | covers the epidermis. | B) | protects the
leaf. | D) | All of the
above |
|
|
|
32
|
The loss of water by the leaves and stem of a plant is called
A) | translocation. | C) | active transport. | B) | osmosis. | D) | transpiration. |
|
|
|
33
|
The guard cells that surround a stoma
A) | have no walls. | B) | swell with water, causing the stoma to
open. | C) | shrivel up when opening the stoma. | D) | are responsible for
translocation. |
|
|
|
34
|
The tissue of the leaf mesophyll that is located directly below the upper
epidermis and consists of tightly packed column-shaped cells is the
A) | palisade layer. | C) | adventitious layer. | B) | cortex. | D) | pith. |
|
|
|
35
|
The flowers produced by angiosperms help ensure the transfer of gametes
by
A) | traveling in the air currents. | B) | bursting open and projecting gametes onto the
landscape. | C) | attracting a particular bird, insect, or other animal. | D) | All of the
above |
|
|
|
36
|
The primary purpose of the fruit is
A) | to provide nutrition for the seed. | C) | seed dispersal. | B) | photosynthesis. | D) | to permit cross-fertilization. |
|