Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
A medical condition that can be treated using proteins produced through genetic
engineering is
a) | hemophilia (treated by promoting blood clotting). | b) | diabetes mellitus
type I. | c) | heart attack (treated by dissolving blood clots). | d) | All of the
above |
|
|
|
2
|
What kind of cell or cells were used to make Dolly?
a) | body cell and egg cell | b) | egg cell only | c) | egg cell and sperm
cell | d) | body cell only |
|
|
|
3
|
Each nucleotide triplet in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid is called
a(n)
a) | exon. | c) | codon. | b) | anticodon. | d) | mutagen. |
|
|
|
4
|
In order for protein synthesis to occur, mRNA must migrate to the
a) | heterochromatin. | c) | RNA polymerase. | b) | lac operon. | d) | ribosomes. |
|
|
|
5
|
The goal of the Human Genome Project is to
a) | create maps showing where chromosomes are located on human genes. | b) | create maps showing
where genes are located on human chromosomes. | c) | treat patients with genetic
diseases. | d) | identify people with genetic diseases. |
|
|
|
6
|
A technique that uses radioactively labeled DNA to identify specific genes in a
piece of DNA is called the
a) | Southern vector. | c) | Northern lights. | b) | Southern blot. | d) | Northern blot. |
|
|
|
7
|
Cloning is a process by which
a) | a virus and a bacterium may be fused into one. | b) | many identical cells
may be produced. | c) | many identical protein fragments are produced. | d) | undesirable genes
may be eliminated. |
|
|
|
8
|
During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is
“rewritten” as a molecule of
a) | messenger RNA. | c) | translation RNA. | b) | ribosomal RNA. | d) | transfer RNA. |
|
|
|
9
|
The function of tRNA is to
a) | transfer amino acids to ribosomes. | c) | synthesize
mRNA. | b) | synthesize DNA. | d) | form ribosomes. |
|
|
|
10
|
Molecules of DNA are composed of long chains of
a) | amino acids. | c) | fatty acids. | b) | monosaccharides. | d) | nucleotides. |
|
|
|
11
|
The enzymes that unwind DNA are called
a) | phages. | c) | double helixes. | b) | forks. | d) | DNA helicases. |
|
|
|
12
|
The amount of thymine in an organism always equals the amount of
a) | cytosine. | c) | adenine. | b) | thymine. | d) | protein. |
|
|
|
13
|
“Genetic engineering” refers to the process of
a) | creating new DNA molecules from nucleotide sequences. | b) | building a new
species by combining genes of different organisms. | c) | moving genes from a chromosome of one organism
to a chromosome of a different organism. | d) | rearranging nucleotides in a gene of an
organism so that new traits appear in the development of an embryo. |
|
|
|
14
|
The anticodons for the codons in the mRNA sequence UACGACUAAGCU
a) | UAC-GAC-UAA-GCU | c) | ATG-CTG-ATT-CGA | b) | TAC-GAC-TAA-GCT | d) | AUG-CUG-AUU-CGA |
|
|
|
15
|
On an electrophoresis gel, band B is closer to the positive end of the gel than
is band A. Which of the following statements is true?
a) | band B moved faster than band A. | b) | band B is more negatively charged than band
A. | c) | band A is smaller than band B. | d) | band B consists of larger DNA fragments than
does band A. |
|
|
|
16
|
Transfer RNA
a) | produces codons to match the correct anticodons. | b) | synthesizes amino
acids as they are needed. | c) | converts DNA into mRNA. | d) | carries an amino
acid to its correct codon. |
|
|
|
17
|
Which of the following is not part of a molecule of DNA?
a) | ribose | c) | phosphate | b) | nitrogen base | d) | deoxyribose |
|
|
|
18
|
The use of genetic engineering to transfer human genes into bacteria
a) | causes the human genes to manufacture bacterial proteins. | b) | results in the
formation of a new species of organism. | c) | allows the bacteria to produce human
proteins. | d) | is impossible with current technology. |
|
|
|
| mRNA codons | amino acid | | UAU, UAC | tyrosine | | CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG | proline | | GAU, GAC | aspartic acid | | AUU, AUC,
AUA | isoleucine | | UGU, UGC | cysteine | | |
|
|
|
19
|
Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino
acids: isoleucine, tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code
given above to determine which of the possible answers contains a DNA sequence that codes for this
amino acid sequence.
a) | AUUUAUCCUGAUUCU | c) | AUUUAACCUGAUUCU | b) | TAAATAGGACTAAGA | d) | TAAATTGGACTAAGA |
|
|
|
20
|
Ian Wilmut’s cloning of Dolly in 1997 was considered a breakthrough in
genetic engineering because
a) | scientists thought cloning was impossible. | b) | scientists had never
before isolated mammary cells. | c) | sheep had never responded well to gene
technology procedures. | d) | scientists though only fetal cells could be
used to produce clones. |
|
|
|
21
|
The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins
are called
a) | exposons. | c) | mutons. | b) | introns. | d) | exons. |
|
|
|
22
|
Each of the following is a type of RNA except
a) | ribosomal RNA. | c) | transfer RNA. | b) | messenger RNA. | d) | carrier RNA. |
|
|
|
23
|
In RNA molecules, adenine is complementary to
a) | cytosine. | c) | guanine. | b) | uracil. | d) | thymine. |
|
|
|
24
|
Enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific places
a) | work only on bacterial DNA. | b) | are restriction enzymes. | c) | always break the DNA
between guanine and adenine. | d) | have sticky
ends. |
|
|
|
25
|
During DNA replication, a complementary strand of DNA is made for each original
DNA strand. Thus, if a portion of the original strand is TTCATAG, then the new strand will be
a) | AAGTATC. | c) | TTCATAG | b) | AACTATG. | d) | GGACGCT. |
|
|
|
26
|
Transferring normal human genes into human cells that lack them
a) | is impossible at this time. | c) | will cause antibodies to kill those
cells. | b) | will cause cancer. | d) | is called human gene therapy. |
|
|
|
27
|
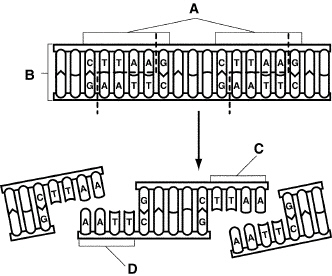
Figure
13-1
What does Figure 13-1 show? a) | DNA sequencing | c) | a restriction enzyme producing a DNA fragment | b) | gel
electrophoresis | d) | polymerase
chain reaction |
|
|
|
28
|
A strand of DNA formed by the splicing of DNA from two different species is
called
a) | plasmid DNA. | c) | restriction RNA. | b) | determinant RNA. | d) | recombinant
DNA. |
|
|
|
29
|
A genome is
a) | a protein fragment. | b) | an organism’s collection of
genes. | c) | the nucleotide sequence that makes up a particular gene. | d) | a fragment of DNA
added to a chromosome during a gene transfer experiment. |
|
|
|
30
|
The scientists credited with establishing the structure of DNA are
a) | Hershey and Chase. | c) | Avery and Chargaff. | b) | Mendel and Griffith. | d) | Watson and
Crick. |
|
|
|
31
|
A nucleotide consists of
a) | a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. | b) | a sugar, a protein,
and adenine. | c) | a starch, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. | d) | a sugar, an amino
acid, and starch. |
|
|
|
32
|
Plasmids
a) | can replicate independently of the organism’s main
chromosome. | b) | are circular pieces of bacterial DNA. | c) | are often used as vectors in genetic
engineering experiments. | d) | All of the
above |
|
|
|
33
|
Which of the following would represent the strand of DNA from which the mRNA
strand in UACGACUAAGCU was made?
a) | ATGCTGATTCGA | c) | TACGACTAAGCT | b) | UACGACUAAGCU | d) | AUGCUGAUUCGA |
|
|
|
34
|
The enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA template bases
are
a) | helicases. | c) | DNA polymerases. | b) | replicases. | d) | restriction
enzymes. |
|
|
|
35
|
RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars have an additional
oxygen atom, and the base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called
a) | cytosine. | c) | codon. | b) | uracil. | d) | alanine. |
|