Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), and nitrogen (N2)
are gases at room temperature. Water (H2O) has a similar molecular weight to these
molecules. Why is H2O a liquid at room temperature?
a. | H2O has a high viscosity. | c. | Adjacent H2O molecules
form hydrogen bonds. | b. | H2O has a high boiling
point. | d. | Nonpolar covalent
bonds hold H2O molecules together. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Lipids are
a. | polar molecules. | c. | water soluble. | b. | similar to water molecules. | d. | nonpolar
molecules. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope used to determine the age of ancient objects
composed of organic matter. Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are other isotopes of carbon. The number of what
subatomic particles varies among these carbon isotopes?
a. | Electrons | c. | Photons | b. | Neutrons | d. | Protons
|
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the following is not an organic macromolecule?
a. | carbohydrate | c. | lipid | b. | ice | d. | nucleic acid |
|
|
|
5.
|
The shape of a protein is primarily determined by
a. | the type and sequence of its amino acids. | b. | its
size. | c. | its cell location. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which functional group found in amino acids is absent from monosaccharides,
polysaccharides, fatty acids, and glycerol?
|
|
|
7.
|
All of the following are examples of carbohydrates except
a. | sugar. | c. | steroids. | b. | cellulose. | d. | glycogen. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Lipids are soluble in
a. | water. | c. | oil. | b. | salt water. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
9.
|
A covalent bond is formed as the result of
a. | transferring electrons. | b. | sharing an electron pair. | c. | transferring
protons. | d. | sharing a proton pair. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which is the LEAST likely trait of an organic molecule?
a. | The molecules may exist as isomers. | c. | Ionic bonds are present between the
atoms. | b. | The backbone is linear, cyclic, or branched. | d. | Functional groups, such as alcohols, are
present. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The two types of nucleic acids are
a. | chlorophyll and retinal. | c. | lipids and
sugars. | b. | DNA and RNA. | d. | glucose and glycogen. |
|
|
|
12.
|
A monosaccharide is a
a. | carbohydrate. | b. | lipid. | c. | nucleic
acid. | d. | protein. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Enzymes affect the reactions in living cells by changing the
a. | products of the reaction. | b. | speed of the reaction. | c. | temperature of the
reaction. | d. | pH of the reaction. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which formula represents an organic molecule?
a. | CuSO4·H2O | c. | AgNO3 | b. | C12H22O11 | d. | H2O |
|
|
|
15.
|
The three particles that make up an atom are
a. | protons, neutrons, and isotopes. | b. | neutrons, isotopes, and
electrons. | c. | positive, negatives, and electrons. | d. | protons, neutrons, and
electrons. |
|
|
|
16.
|
As part of an experiment, a student adds 10 mL of 5% hydrochloric acid solution
to 100 mL of a non-buffered, colorless solution of sugar. What is the most likely result?
a. | The concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) will increase. | c. | The pH will not
change. | b. | The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) will increase. | d. | The pH will
increase. |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the primary factor that determines the polarity of a bond between
atoms?
a. | The total number of electrons involved in the bond | c. | The difference in the relative
attraction of electrons to each atom | b. | The total number of protons and neutrons in
both atoms | d. | The difference
in the relative attraction of protons to each atom |
|
|
|
18.
|
When the pH in a stomach increases from 2 to 4, how does the hydrogen ion
concentration change?
a. | It increases by a factor of 2. | c. | It decreases by a factor of
2. | b. | It increases by a factor of 100. | d. | It decreases by a factor of
100. |
|
|
|
19.
|
A substance with a pH of 6 is called
a. | an acid. | b. | a base. | c. | both an acid and a
base. | d. | neither an acid nor a base. |
|
|
|
20.
|
What is the term used to describe the energy needed to get a reaction
started?
a. | adhesion energy | b. | activation energy | c. | cohesion
energy | d. | chemical energy |
|
|
|
21.
|
Two students conduct an experiment in which they measure the concentration of an
enzyme in a test tube at 1 minute intervals over the course of an enzymatic reaction. Each of the
students makes a prediction about what will happen to the enzyme concentration as the reaction
progresses. Student 1 predicts that the concentration of the enzyme in the test tube will decrease as
the reaction progresses. Student 2 predicts that the concentration of the enzyme in the test tube
will stay the same as the reaction progresses. Which student’s prediction is correct, and
why?
a. | Student 1; enzymes are depleted as a reaction progresses. | c. | Student 2; enzymes
are depleted as a reaction progresses. | b. | Student 1; enzymes are not depleted as a
reaction progresses. | d. | Student 2; enzymes are not depleted as a reaction
progresses. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The molecule on which an enzyme acts is called a(n)
a. | active site. | c. | organic molecule. | b. | inactive site. | d. | substrate. |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the maximum number of covalent bonds that can form between a single
carbon atom and 1 or more hydrogen atoms?
|
|
|
24.
|
When salt is dissolved in water, water is the
a. | reactant. | b. | solution. | c. | solute. | d. | solvent. |
|
|
|
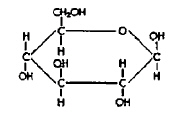  Molecule
A
Molecule B
|
|
|
25.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Molecules like Molecule “B” are
found in
a. | carbohydrates. | c. | nucleic acids. | b. | lipids. | d. | proteins. |
|
|
|
26.
|
In chemical reactions, atoms are
a. | created. | b. | destroyed. | c. | rearranged. | d. | neutralized. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Jenna’s favorite breakfast food, papaya, contains significant amounts of
the enzyme papain (a protease). What substances does papain help digest?
a. | Carbohydrates | c. | Nucleic acids | b. | Fatty acids | d. | Proteins |
|
|
|
28.
|
Long chains of amino acids are found in
a. | carbohydrates. | c. | proteins. | b. | lipids. | d. | sugars. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which solution has the greatest concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-)
?
a. | Urine (pH 6.0) | c. | Tomato juice (pH 4.0) | b. | Rainwater (pH
5.5) | d. | Gastric juice (pH
2.0) |
|
|
|
30.
|
Breaking which type of bond would require the most energy?
a. | Covalent | c. | Hydrogen | b. | Electrostatic | d. | Intermolecular |
|
|
|
31.
|
Pepsin is a protein-digesting enzyme in the human stomach. Antacids cause the pH
of the stomach to increase and protein digestion becomes less efficient. What occurs to reduce the
efficiency of protein digestion?
a. | Antacids break the covalent bonds within pepsin. | c. | The active site of pepsin changes
shape. | b. | Pepsin dissolves antacids in the gastric juice. | d. | The concentration of pepsin
increases. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Nonpolar molecules have
a. | no negative or positive poles. | c. | only a negative
pole. | b. | both negative and positive poles. | d. | only a positive
pole. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Ionic bonds form between molecules that have
a. | opposite charges. | c. | no charges. | b. | the same charge. | d. | neutral
charges. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Why are organic molecules so diverse?
a. | They form mirror images of each other. | c. | They form when any naturally
occurring elements combine. | b. | They contain oxygen, which has 6 valence
electrons. | d. | They have carbon
skeletons that vary greatly in arrangement. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Hydrogen ions, H+, react with hydroxide ions, OH–,
to form
a. | water. | c. | a base. | b. | an acid. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
36.
|
Identify the reactant(s) in the chemical reaction, CO2 +
H2O ® H2CO3.
a. | CO2, H2O, and H2CO3 | b. | CO2 and
H2O | c. | H2CO3 | d. | CO2 |
|
|
|
37.
|
Lead (Pb-208) is the heaviest stable isotope known. It has an atomic number of
82. How many neutrons does Pb-208 have?
|
|
|
38.
|
Water is a polar molecule because
a. | it contains two hydrogen atoms for each oxygen atom. | b. | it has a
charge. | c. | different parts of the molecule have slightly different charges. | d. | it does not have a
charge. |
|
|
|
39.
|
The nucleus is made up of
a. | protons and electrons. | b. | electrons and neutrons. | c. | protons and
neutrons. | d. | protons, neutrons, and electrons. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following statements about enzymes is NOT true?
a. | Enzymes work best at a specified pH. | b. | All enzymes work inside
cells. | c. | Enzymes are proteins. | d. | Enzymes are organic
catalysts. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Cosmetics often contain glycerol (C3H8O3),
which has three identical functional groups. Which type of bond holds these functional groups
together?
a. | Covalent | c. | Intermolecular | b. | Hydrogen | d. | Ionic |
|
|
|
42.
|
a. | serve as food reserves in many organisms | c. | include fats that are broken down
into one fatty acid molecule and three glycerol molecules | b. | include cartilage
and chitin | d. | are composed of
monosaccharides |
|
|
|
43.
|
Starch and cellulose are alike in that both
are: a. | composed of covalently bonded glucose molecules | c. | contain sugars bonded together in
identical ways | b. | found only in animal cells
| d. | contain non-polar, fatty acid side
chains |
|
|
|
44.
|
A(n) ____________ is a basic unit of a
carbohydrate. a. | monosaccharide | c. | glycerol | b. | amino acid | d. | nucleotide |
|