Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
The structure labeled e
a) | contains sperm cells. | b) | contains ovules | c) | is the area where pollen
lands on and sticks. | d) | produces
pollen. |
|
|
|
2
|
The structure indicated at f
a) | develops into a fruit. | c) | produces
pollen. | b) | supports the pistil. | d) | supports the
anther. |
|
|
|
3
|
Lamila wants to determine the rate at which a plant uses
water. She fills a beaker with 80 mL of water and places a leafy flower stem into the beaker through
a small opening in the beaker’s cap. Lamila then places the beaker near a sunny window. One
week later, 47 mL of water remains in the beaker.What plant process best explains the loss of water
in the beaker?
a) | Germination | c) | Respiration | b) | Photosynthesis | d) | Transpiration |
|
|
|
4
|
Vascular tissue in plants consists of
a) | meristem. | b) | parenchyma and collenchyma
cells. | c) | epidermal cells. | d) | xylem and phloem. |
|
|
|
5
|
Angiosperms produce seeds inside protective structures
called
a) | pollen grains. | b) | petals. | c) | cones. | d) | ovaries. |
|
|
|
6
|
The part of a seed that develops into the first roots is
the
a) | plumule. | b) | cotyledon. | c) | testa. | d) | radicle. |
|
|
|
7
|
The cotyledons in a seed
a) | are part of the gametophyte. | b) | protect the embryo. | c) | provide a source of food
for the embryo. | d) | develop from the seed
coat. |
|
|
|
8
|
The xylem in a plant
a) | transports food from the leaves. | b) | transports water and minerals. | c) | exchanges carbon dioxide
with the atmosphere. | d) | performs
photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
The diagram below shows a leaf cross section. 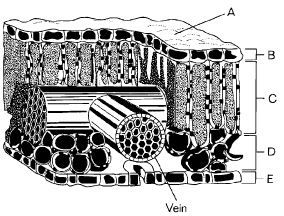
|
|
|
9
|
Refer to the illustration above. The vein illustrated is made up of
a) | only xylem vessels. | c) | only phloem vessels. | b) | both xylem and phloem
vessels. | d) | neither xylem nor
phloem vessels. |
|
|
|
10
|
Refer to the illustration above. Structure A
a) | transports materials | c) | protects the leaf from dehydration | b) | performs
photosynthesis | d) | allows gas
exchange |
|
|
|
11
|
Refer to the illustration above. The palisade layer is indicated at
|
|
|
12
|
A flower is a
a) | vegetative structure. | c) | homologous
structure. | b) | reproductive
structure. | d) | photosynthetic structure. |
|
|
|
13
|
A ripened ovary that contains seeds is called
a(an)
a) | seed. | b) | embryo. | c) | fruit. | d) | vegetable. |
|
|
|
14
|
Hummingbirds transfer pollen from one flower to another
while feeding. What plant structure contains the pollen?
a) | Stamen | c) | Petal | b) | Sepal
| d) | Carpel |
|
|
|
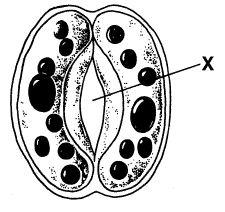
Figure 23-2
|
|
|
15
|
In Figure 23-2, the water pressure in the
a) | guard cells is high. | b) | guard cells is low. | c) | stoma is
high. | d) | stoma is low. |
|
|
|
16
|
In Figure 23-2, the structure labeled X is
a
a) | guard cell | b) | stoma | c) | mesophyll
cell | d) | vein |
|
|
|
17
|
The photosynthetic tissue of the leaf is called
__________.
a) | mesophyll | c) | epidermis | b) | cortex
| d) | cuticle |
|
|
|
18
|
The waxy protective covering of a land plant is called
a
a) | capsule. | c) | stoma. | b) | cuticle. | d) | rhizome. |
|
|
|
19
|
The leaf-like structure that protects the budding flower is
called the:
a) | Style | c) | Petal | b) | Anther | d) | Sepal |
|
|
|
20
|
The phloem in a plant
a) | transports sugars. | b) | transports water and minerals. | c) | exchanges carbon dioxide
and oxygen with the atmosphere. | d) | performs
photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
21
|
What structures compose the corolla of a
flower?
a) | petals | c) | stamens | b) | pistils | d) | sepals |
|
|
|
22
|
In an angiosperm, ovules are produced in the
a) | filament. | b) | anther. | c) | stigma. | d) | pistil. |
|
|
|
23
|
The loss of water by the leaves and stem of a plant is
called
a) | translocation. | c) | osmosis. | b) | active
transport. | d) | transpiration. |
|
|
|
24
|
Adam visits Redwood National Park and learns that redwood
trees grow to heights of more than 100 m. How do trees get water and nutrients from the soil to their
tops?
a) | Transpiration from the leaves pulls water
upward. | c) | Gravity continually pulls water and nutrients
upward. | b) | Trees use energy from ATP to push water and nutrients
upward. | d) | Xylem contract and push water and nutrients
upward. |
|
|
|
25
|
The guard cells that surround a stoma
a) | shrivel up when opening the stoma. | b) | have no walls. | c) | are responsible for
translocation. | d) | swell with water, causing
the stoma to open. |
|