Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The major atmospheric by-product of photosynthesis is
a. | nitrogen. | c. | oxygen. | b. | water. | d. | carbon dioxide. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Plants gather the sun's energy with light-absorbing structures
called
a. | mitochondria. | b. | glucose. | c. | pigments. | d. | chloroplasts. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following is released during cellular respiration?
a. | air | b. | energy | c. | lactic
acid | d. | oxygen |
|
|
|
4.
|
What are the reactants in the equation for cellular respiration?
a. | oxygen and lactic acid | c. | glucose and oxygen | b. | carbon dioxide and water | d. | water and
glucose |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following is not part of cellular respiration?
a. | electron transport | c. | Krebs cycle | b. | glycolysis | d. | Calvin cycle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Graph A demonstrates that the rate of
photosynthesis
a. | increases indefinitely in response to increasing light intensity. | b. | increases in
response to increasing light intensity, but only to a certain point. | c. | decreases in
response to increasing light intensity. | d. | is unaffected by changes in light
intensity. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Cellular respiration releases energy by breaking down
a. | food molecules. | b. | ATP. | c. | water. | d. | carbon dioxide. |
|
|
|
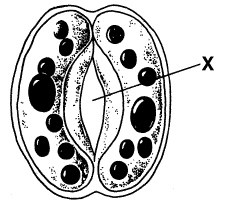
Figure
23-2
|
|
|
8.
|
In Figure 23-2, the X points to a
a. | stoma. | b. | mesophyll cell. | c. | vein. | d. | guard cell. |
|
|
|
9.
|
What are the products of the Calvin cycle?
a. | light | b. | oxygen gas | c. | high-energy
sugars | d. | ATP |
|
|
|
10.
|
The products of photosynthesis are the
a. | products of glycolysis. | b. | products of cellular
respiration. | c. | reactants of fermentation. | d. | reactants of cellular
respiration. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into
a. | oxygen. | b. | high-energy sugars. | c. | oxygen and
high-energy sugars. | d. | ATP and oxygen. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Organisms, such as plants, that make their own food are called
a. | thylakoids. | b. | autotrophs. | c. | heterotrophs. | d. | pigments. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in cellular
respiration?
a. | glycolysis ® Krebs cycle ® electron transport | b. | Krebs cycle ® glycolysis ® electron
transport | c. | Krebs cycle ® electron transport ® glycolysis | d. | glycolysis ®
fermentation ® Krebs cycle |
|
|
|
The questions below refer to the following balanced chemical
equation.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + ADP + P ® 6CO2 + 6 H2O + MOLECULE A
|
|
|
14.
|
Refer to the equation above. The process summarized by the equation begins in
the cytoplasm of a cell and ends in the
a. | endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | cytoplasm. | b. | cell membrane. | d. | mitochondria. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following is an autotroph?
a. | mushroom | b. | dog | c. | monkey | d. | tree |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the source of energy that provides the boost for electrons during
photosynthesis?
a. | water | c. | light | b. | cellular respiration | d. | ATP |
|
|
|
17.
|
The source of oxygen produced during photosynthesis is
a. | carbon dioxide. | c. | glucose. | b. | the air. | d. | water. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Cells produce ATP most efficiently in the presence of
a. | glucose. | c. | oxygen. | b. | water. | d. | carbon dioxide. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Milk is converted to yogurt under certain conditions when the microorganisms in
the milk produce acid. Which of these processes would you expect to be key in the production of
yogurt?
a. | photosynthesis | b. | lactic acid fermentation | c. | the Krebs
cycle | d. | alcoholic fermentation |
|
|
|
20.
|
During photosynthesis, the series of reactions that create the complex
carbohydrates needed for energy and growth is called
a. | the electron transport chain. | c. | the Calvin
cycle. | b. | the Krebs cycle. | d. | the Hobbs cycle. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Chloroplasts contain disklike membranous sacs arranged in stacks called
a. | vacuoles. | c. | thylakoids. | b. | stoma. | d. | cholorphyll. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which process does NOT release energy from glucose?
a. | glycolysis | b. | cellular respiration | c. | photosynthesis | d. | fermentation |
|
|
|
23.
|
One cause of muscle soreness is
a. | the Krebs cycle. | b. | glycolysis. | c. | lactic acid
fermentation. | d. | alcoholic fermentation. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Vascular tissue in plants consists of
a. | xylem and phloem. | b. | meristem. | c. | epidermal
cells. | d. | parenchyma and collenchyma cells. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Heterotrophs obtain the energy they need for metabolism through
a. | glycolysis. | c. | cellular respiration. | b. | osmosis. | d. | photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Light energy is converted to chemical energy through the process of
a. | glycolysis. | c. | photosynthesis. | b. | fermentation. | d. | cellular
respiration. |
|
|
|
27.
|
If oxygen is absent during the second stage of cellular respiration,
a. | the Krebs cycle begins. | b. | glycolysis stops. | c. | the electron
transport chain works more efficiently. | d. | fermentation will
occur. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Cellular respiration takes place in three stages:
a. | Calvin Cycle, electron transport chain, then glycolysis. | b. | glycolysis,
fermentation, then electron transport chain | c. | Krebs Cycle, electron transport chain, then
fermentation. | d. | glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, then electron transport
chain. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Most of the energy used by life on Earth comes from
a. | the rotation of the Earth. | c. | the sun. | b. | the
moon. | d. | nuclear
energy. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Energy is released from ATP when
a. | ATP is exposed to sunlight. | b. | adenine bonds to ribose. | c. | a phosphate group is
removed. | d. | a phosphate group is added. |
|