Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
Natural selection is the process by which
a) | the age of selected fossils is calculated. | b) | acquired traits are
passed on from one generation to the next. | c) | organisms with traits well suited to their
environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than less well-adapted organisms in the same
environment. | d) | organisms least suited to their environment survive and pass on their
traits. |
|
|
|
2
|
According to fossil evidence, whales evolved from 4-legged ancestors. The modern
baleen whale has forelimbs, but inspection of its skeleton reveals only tiny vestigial hind limbs.
What is the best explanation for this loss of hind limbs in the baleen whale?
a) | Some whales lost longer hind limbs to predators and passed that trait to their
offspring. | c) | Whales with shorter hind limbs swam faster than those with longer hind
limbs. | b) | Random chance and genetic drift led to the reduction in size of hind
limbs. | d) | The hind limbs
adapted into flippers to help the whale swim faster. |
|
|
|
3
|
The fitness of individuals with an average form of a phenotypic trait is highest
in
a) | natural selection. | b) | directional selection. | c) | stabilizing
selection. | d) | disruptive selection. |
|
|
|
4
|
Which of the following is a vestigial structure?
a) | the human tailbone | c) | flower color | b) | fossil cast | d) | the bill of a
finch |
|
|
|
5
|
The type of selection that may eliminate intermediate phenotypes is
a) | disruptive selection. | c) | direction selection. | b) | stabilizing selection. | d) | polygenic
selection. |
|
|
|
6
|
When comparing 2 populations of animals, which statement most likely indicates
that they are the same species?
a) | Their outward appearance is similar. | c) | They consume the same type of
diet. | b) | They inhabit the same general area. | d) | They produce fertile
offspring. |
|
|
|
7
|
Which is a major concept included in Lamarck's theory of evolution?
a) | Body structure can change according to the needs of the organism. | b) | Change is the result
of mutations. | c) | Selection pressures decrease the rate of evolution. | d) | Sexual reproduction
is the genetic basis for variations. |
|
|
|
8
|
The wings of experimental fruit flies were clipped short each generation for
fifty generations. The fifty-first generation emerged with normal-length wings. This observation
would tend to disprove the theory of evolution based on
a) | survival of the fittest. | b) | inheritance of mutations. | c) | natural
selection. | d) | inheritance of acquired characteristics. |
|
|
|
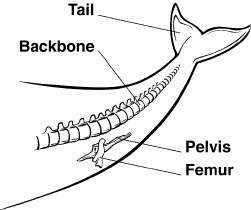
Figure
15-2
|
|
|
9
|
The pelvis and femur of the whale shown in Figure 15-2
a) | are vestigial structures. | b) | are not inherited. | c) | allow the whale to
walk. | d) | are acquired traits. |
|
|
|
10
|
Most male crickets produce a mating song by rubbing together their curved wings.
In a certain geographic area, parasitic flies detected male crickets singing and deposited their
larvae into them, which killed the crickets. Eighteen generations later the number of males with flat
wings has increased to 90%. The flat-winged crickets do not sing, but are still able to mate with
females, and parasitic flies cannot detect them. Which type of selection is occurring in this cricket
population?
a) | Disruptive | c) | Directional | b) | Artificial | d) | Stabilizing |
|
|
|
11
|
According to Darwin's theory of natural selection, individuals who survive
are most likely the ones best adapted to exist in their environment. Their survival is due to
the
a) | lack of competition within the species. | b) | possession of
structures developed through use. | c) | possession of adaptations that maximize
fitness. | d) | ability to change their genotype. |
|
|
|
12
|
Beak shape in finches is affected by
a) | the color of the finch. | c) | the number of predators in the
area. | b) | the size of the finch. | d) | the availability of food. |
|
|
|
13
|
When lions prey on a herd of antelope, some antelope are eliminated. Which part
of Darwin's theory of evolution may be used to describe this situation?
a) | acquired characteristics | b) | speciation due to mutations | c) | reproductive
isolation | d) | survival of the fittest |
|
|
|
14
|
Dinosaur species dominated Earth for over 100 million years. During this time,
most mammals were small mouse-sized nocturnal organisms. Following the mass extinction of the
dinosaurs, the small mammals rapidly diversified to fill available habitats and niches. What pattern
of evolution best explains the diversification of mammals?
a) | Gradualism | c) | Convergent evolution | b) | Catastrophism | d) | Punctuated
equilibrium |
|
|
|
15
|
Populations are separated by barriers such as rivers, mountains, or bodies of
water in
a) | temporal isolation. | b) | natural selection. | c) | behavioral
isolation. | d) | geographic isolation. |
|
|
|
16
|
A change in the frequency of a particular gene in one direction in a population
is called
a) | acquired variation. | c) | directional selection. | b) | chromosome
drift. | d) | balancing
selection. |
|
|
|
17
|
The American toad breeds earlier in the spring than the Fowler's toad does.
Therefore, they do not interbreed, even though they often live in the same habitat. What can be
inferred from this information?
a) | The two species do not interbreed because of temporal isolation. | b) | Fowler's toad
has a higher rate of survival than the American toad does. | c) | The two species do
not interbreed because of geographic isolation. | d) | The two species undergo no ecological
competition. |
|
|
|
18
|
In a population of finches in which one subset of birds has a short, parrotlike
beak and a second subset has a long, narrow beak, what process has probably occurred?
a) | stabilizing selection | b) | directional selection | c) | disruptive
selection | d) | genetic drift |
|
|
|
|
|
|
19
|
Refer to the illustration above. An analysis of DNA from these organisms would
indicate that
a) | they all have gill pouches. | b) | they have identical DNA. | c) | they all have the
same number of chromosomes. | d) | their nucleotide sequences show many
similarities. |
|
|
|
20
|
Refer to the illustration above. The bones labeled A are known as
a) | sequential structures. | c) | fossil structures. | b) | homologous structures. | d) | vestigial
structures. |
|
|
|
21
|
Natural selection could not occur without
a) | genetic variation in species. | c) | gradual warming of the
Earth. | b) | environmental changes. | d) | competition for unlimited resources. |
|
|
|
22
|
The hypothesis that evolution occurs at a slow, constant rate is known as
a) | adaptation. | c) | slow motion. | b) | gradualism. | d) | natural
selection. |
|
|
|
23
|
What accounts for genetic biodiversity existing in modern multicellular
organisms?
a) | Somatic cell DNA mutations create new phenotypes in the population. | c) | Genetic mutations
form when similar species mate and reproduce. | b) | Protein mutations cause DNA changes, creating
new species. | d) | Mutations in
gametes are passed to offspring. |
|
|
|
24
|
According to Darwin's theory of natural selection, the individuals that
tend to survive are those that have
a) | undergone mutations. | b) | the smallest number of
offspring. | c) | characteristics their parents acquired by use and disuse. | d) | variations best
suited to the environment. |
|
|
|
25
|
Starfish larvae resemble some primitive vertebrate larvae. This similarity may
be used to suggest that primitive vertebrates
a) | evolved before starfish. | b) | belong to the same population as
starfish. | c) | evolved from modern-day starfish. | d) | share a common ancestor with
starfish. |
|
|
|
26
|
Dinosaur extinction coincided with a massive asteroid’s collision with
Earth. The extreme heat of the impact killed many organisms. The resulting dust cloud prevented
photosynthesis for a long period of time, killing many other organisms. Which scenario most likely
explains how life survived on Earth after the asteroid impact?
a) | Some organisms survived the initial impact and adapted to new food sources and
habitats. | c) | The large number of dead organisms supplied an abundant food source for surviving
carnivores. | b) | The dust cloud affected terrestrial organisms, but did not affect aquatic
organisms. | d) | Microscopic
organisms survived and evolved into modern forms of terrestrial and aquatic
life. |
|
|
|
27
|
To compare the relative ages of fossils, scientists use an easily recognized
species called a(an)
a) | carbon fossil. | b) | index fossil. | c) | sedimentary
fossil. | d) | radioactive fossil. |
|
|
|
28
|
The major idea that Darwin presented in his book The Origin of Species
was that
a) | animals changed, but plants remained the same. | b) | species changed over
time and never competed with each other. | c) | giraffes and peppered moths changed
constantly. | d) | species changed over time by natural selection. |
|
|
|
29
|
Darwin thought that the plants and animals of the Galapagos Islands were similar
to those of the nearby coast of South America because
a) | he found fossils proving that the animals and plants had common
ancestors. | b) | they had all been created by God to match their habitat. | c) | their ancestors had
migrated from South America to the Galapagos Islands. | d) | the island organisms had the same nucleotide
sequences in their DNA as the mainland organisms. |
|
|
|
A Comparison of Dolphins and
Sharks 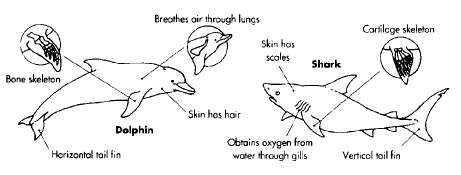
|
|
|
30
|
Refer to the illustration above. While the shark and dolphin are similar in
appearance, they evolved independently. This is an example of
a) | convergent evolution. | c) | divergent evolution. | b) | phenetics. | d) | cladistics. |
|