Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
The amount of guanine in an organism always equals the amount of
A) | protein. | C) | adenine. | B) | thymine. | D) | cytosine. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
The entire molecule shown in the diagram is called a(n)
A) | amino acid. | C) | nucleotide. | B) | pyrimidine. | D) | polysaccharide. |
|
|
|
3
|
During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is
“rewritten” as a molecule of
A) | transfer RNA. | C) | ribosomal RNA. | B) | translation RNA. | D) | messenger RNA. |
|
|
|
4
|
A genome is
A) | the nucleotide sequence that makes up a particular gene. | B) | a fragment of DNA
added to a chromosome during a gene transfer experiment. | C) | a protein
fragment. | D) | an organism’s collection of genes. |
|
|
|
5
|
Enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific places
A) | are restriction enzymes. | B) | have sticky ends. | C) | always break the DNA
between guanine and adenine. | D) | work only on bacterial
DNA. |
|
|
|
6
|
Which of the following were able to show that DNA wasa helix or spiral
shape?
A) | Wilkins and Franklin | C) | Watson and Crick | B) | Hershey and Chase | D) | Chargaff |
|
|
|
7
|
The part of the molecule for which deoxyribonucleic acid is named is the
A) | phosphate group. | C) | nitrogen base. | B) | sugar. | D) | None of the
above |
|
|
|
Use the diagram below of a strand of an mRNA and the genetic code shown there to
answer the following questions:
mRNA:
CUCAAGUGCUUC Genetic Code: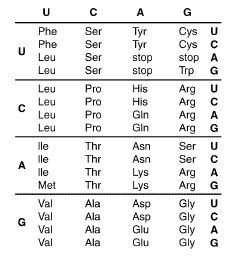
|
|
|
8
|
Refer to the illustration above. What is the portion of the protein molecule
coded for by the piece of mRNA shown in the diagram?
A) | Val—Asp—Pro—His | C) | Leu—Lys—Cys—Phe | B) | Ser—Tyr—Arg—Gly | D) | Pro—Glu—Leu—Val |
|
|
|
9
|
Which of the following would represent the strand of DNA from which the mRNA
strand in the diagram was made?
A) | CUCAAGUGCUUC | C) | GAGUUCACGAAG | B) | GAGTTCACGAAG | D) | AGACCTGTAGGA |
|
|
|
10
|
The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins
are called
A) | mutons. | C) | exposons. | B) | introns. | D) | exons. |
|
|
|
11
|
A nucleotide consists of
A) | a sugar, a protein, and adenine. | B) | a sugar, an amino acid, and
starch. | C) | a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. | D) | a starch, a
phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. |
|
|
|
12
|
In order for protein synthesis to occur, mRNA must migrate to the
A) | ribosomes. | C) | RNA polymerase. | B) | heterochromatin. | D) | lac
operon. |
|
|
|
13
|
The enzymes that unwind DNA are called
A) | DNA helicases. | C) | phages. | B) | forks. | D) | double helixes. |
|
|
|
14
|
Which of the following is not part of a molecule of RNA?
A) | nitrogen base | C) | ribose | B) | deoxyribose | D) | phosphate |
|
|
|
15
|
RNA is chemically similar to DNA except that its sugars have an additional
oxygen atom, and the base thymine is replaced by a structurally similar base called
A) | alanine. | C) | uracil. | B) | cytosine. | D) | codon. |
|
|
|
16
|
In RNA molecules, adenine is complementary to
A) | guanine. | C) | cytosine. | B) | uracil. | D) | thymine. |
|
|
|
17
|
Molecules of DNA are composed of long chains of
A) | amino acids. | C) | nucleotides. | B) | monosaccharides. | D) | fatty acids. |
|
|
|
| mRNA codons | amino acid | | UAU, UAC | tyrosine | | CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG | proline | | GAU, GAC | aspartic acid | | AUU, AUC,
AUA | isoleucine | | UGU, UGC | cysteine | | |
|
|
|
18
|
Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino
acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic
code given above to determine which of the possible answers contains a DNA sequence that codes for
this amino acid sequence.
A) | AUGGGUCUAUAUACG | C) | ATAGGGCTTTAAACA | B) | ATGGGTCTATATACG | D) | GCAAACTCGCGCGTA |
|
|
|
19
|
The enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA template bases
are
A) | helicases. | C) | replicases. | B) | DNA polymerases. | D) | None of the
above |
|
|
|
20
|
Cloning is a process by which
A) | undesirable genes may be eliminated. | B) | a virus and a bacterium may be fused into
one. | C) | many identical protein fragments are produced. | D) | genetically
identical copies may be produced. |
|
|
|
21
|
Each nucleotide triplet in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid is called
a(n)
A) | exon. | C) | mutagen. | B) | codon. | D) | anticodon. |
|
|
|
22
|
The non-coding portions of DNA that are separated from the portions of DNA
actually used during transcription are called
A) | exposons. | C) | mutons. | B) | exons. | D) | introns. |
|
|
|
23
|
The function of rRNA is to
A) | transfer amino acids to ribosomes. | C) | assemble proteins from amino
acids | B) | form ribosomes. | D) | synthesize DNA. |
|
|
|
24
|
During DNA replication, a complementary strand of DNA is made for each original
DNA strand. Thus, if a portion of the original strand is CCTAGCT, then the new strand will be
A) | AAGTATC. | C) | TTGCATG. | B) | CCTAGCT. | D) | GGATCGA. |
|
|
|
25
|
Transfer RNA
A) | produces codons to match the correct anticodons. | B) | carries an amino
acid to its correct codon. | C) | converts DNA into mRNA. | D) | synthesizes amino
acids as they are needed. |
|