Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
The three particles that make up an atom are [A.5.a]
a) | protons, neutrons, and electrons. | b) | positive, negatives, and
electrons. | c) | neutrons, isotopes, and electrons. | d) | protons, neutrons, and
isotopes. |
|
|
|
2
|
Breaking which type of bond would require the most energy?
[A.5.c]
a) | Covalent | c) | Hydrogen | b) | Electrostatic | d) | Intermolecular |
|
|
|
3
|
What key factor distinguishes organic compounds from inorganic compounds?
[A.5.e]
a) | Organic compounds provide energy for cells. | c) | Organic compounds are the building
blocks of cells. | b) | Organic compounds contain hydrogen. | d) | Organic compounds contain
carbon. |
|
|
|
4
|
The double arrows tell you that the following reaction
CO2 + H2O D H2CO3
[A.5.d]
a) | a. takes place very rapidly. | c) | has high bond
energies. | b) | is very unstable. | d) | occurs in both directions. |
|
|
|
5
|
What is the term used to describe the energy needed to get a reaction started?
[A.5.h]
a) | cohesion energy | b) | activation energy | c) | adhesion
energy | d) | chemical energy |
|
|
|
6
|
Two students conduct an experiment in which they measure the concentration of an
enzyme in a test tube at 1 minute intervals over the course of an enzymatic reaction. Each of the
students makes a prediction about what will happen to the enzyme concentration as the reaction
progresses. Student 1 predicts that the concentration of the enzyme in the test tube will decrease as
the reaction progresses. Student 2 predicts that the concentration of the enzyme in the test tube
will stay the same as the reaction progresses. Which student’s prediction is correct, and why?
[A.5.h]
a) | Student 2; enzymes are not depleted as a reaction progresses. | c) | Student 1; enzymes
are not depleted as a reaction progresses. | b) | Student 2; enzymes are depleted as a reaction
progresses. | d) | Student 1;
enzymes are depleted as a reaction progresses. |
|
|
|
7
|
A covalent bond is formed as the result of [A.5.c]
a) | transferring electrons. | b) | sharing an electron pair. | c) | transferring
protons. | d) | sharing a proton pair. |
|
|
|
8
|
Of the following functional groups, which one is
known as the amino group? [A.5.g]
|
|
|
9
|
Identify the reactant(s) in the chemical reaction, CO2 +
H2O ®H2CO3. [A.5.d]
a) | CO2, H2O, and H2CO3 | b) | CO2 and
H2O | c) | H2CO3 | d) | CO2 |
|
|
|
10
|
Which formula represents an organic molecule? [A.5.e]
a) | H2O | c) | AgNO3 | b) | C12H22O11 | d) | CuSO4·H2O |
|
|
|
11
|
Long chains of amino acids are found in [A.5.g]
a) | sugars. | c) | carbohydrates. | b) | lipids. | d) | proteins. |
|
|
|
12
|
The attraction among molecules of the same substance, such as water, is called
[A.5.i]
a) | cohesion. | c) | adhesion. | b) | surface tension. | d) | specific heat. |
|
|
|
13
|
Which category of carbon-based molecules includes sugars and starches?
[A.5.g]
a) | proteins | c) | phospholipids | b) | unsaturated fatty acids | d) | carbohydrates |
|
|
|
14
|
The two types of nucleic acids are [A.5.g]
a) | glucose and glycogen. | c) | lipids and sugars. | b) | DNA and RNA. | d) | chlorophyll and
retinal. |
|
|
|
15
|
How are atoms and ions different? [A.5.b]
a) | atoms have unequal numbers of protons and electrons | c) | atoms are charged while ions
aren’t | b) | ions have unequal numbers of protons and electrons | d) | nothing, they are two different names for the
same thing |
|
|
|
16
|
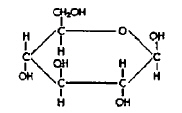 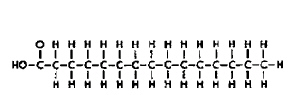
Molecule A
Molecule B Refer to the illustration above. Molecules like Molecule “A” are found in
[A.5.g] a) | carbohydrates. | c) | nucleic acids. | b) | lipids. | d) | proteins. |
|
|
|
17
|
Which solution has the lowest concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) ?
[A.5.f]
a) | Urine (pH 6.0) | c) | Tomato juice (pH 4.0) | b) | Gastric juice (pH
2.0) | d) | Rainwater (pH
5.5) |
|
|
|
18
|
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions? [A.5.h]
a) | By reducing activation energy | c) | By reducing energy produced by the
reaction | b) | By increasing activation energy | d) | By increasing energy produced by the
reaction |
|
|
|
19
|
A solution with a pH of 4 is [A.5.f]
a) | basic. | c) | acidic. | b) | a buffer. | d) | neutral. |
|
|
|
20
|
The shape of a protein is primarily determined by [A.5.g]
a) | its cell location. | b) | the type and sequence of its amino
acids. | c) | its size. | d) | None of the
above |
|
|
|
21
|
The molecule on which an enzyme acts is called a(n) [A.5.h]
a) | active site. | c) | substrate. | b) | inactive site. | d) | organic
molecule. |
|
|
|
22
|
The electrons of an atom [A.5.a]
a) | orbit the nucleus in various energy levels. | b) | are attracted to the
positive charge of neutrons. | c) | have a positive charge. | d) | are found in the
nucleus along with the protons. |
|
|
|
23
|
In chemical reactions, atoms are [A.5.d]
a) | neutralized. | b) | destroyed. | c) | created. | d) | rearranged. |
|
|
|
24
|
When the pH in a stomach changes from 4 to 2, how does the hydrogen ion
concentration change? [A.5.f]
a) | It increases by a factor of 2. | c) | It decreases by a factor of
2. | b) | It increases by a factor of 100. | d) | It decreases by a factor of
100. |
|
|
|
25
|
Which of the following organic compounds is the main source of energy for living
things? [A.5.g]
a) | nucleic acids | b) | proteins | c) | lipids | d) | carbohydrates |
|
|
|
26
|
What is the primary factor that determines the polarity of a bond between atoms?
[A.5.c]
a) | The total number of electrons involved in the bond | c) | The difference in the relative
attraction of electrons to each atom | b) | The total number of protons and neutrons in
both atoms | d) | The difference
in the relative attraction of protons to each atom |
|
|
|
27
|
Enzymes affect chemical reactions in living organisms by
[A.5.h]
a) | breaking down molecules into starch. | c) | changing the direction of a
reaction. | b) | weakening bonds in reactants. | d) | increasing the temperature
range. |
|
|
|
28
|
Methane (CH4), oxygen (O2), and nitrogen (N2)
are gases at room temperature. Water (H2O) has a similar molecular weight to these
molecules. Why is H2O a liquid at room temperature? [A.5.i]
a) | H2O has a high boiling point. | c) | Nonpolar covalent bonds hold
H2O molecules together. | b) | H2O has a high
viscosity. | d) | Adjacent
H2O molecules form hydrogen bonds. |
|
|
|
29
|
The names of all sugars end in [A.5.g]
|
|
|
30
|
The smallest basic unit of matter is the [A.5.a]
a) | molecule. | c) | compound. | b) | atom. | d) | cell. |
|