Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The double membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the
a. | nucleolus. | c. | ribosome. | b. | nuclear wall. | d. | nuclear
envelope. |
|
|
|
2.
|
All the following are found in both plant and animal cells, except
a. | a cell wall. | c. | mitochondria. | b. | a cell membrane. | d. | endoplasmic
reticulum. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which organelle converts food into compounds that the cell uses for growth,
development, and movement?
a. | chloroplast | b. | Golgi apparatus | c. | endoplasmic
reticulum | d. | mitochondrion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which structure immediately identifies this
cell as a eukaryote?
a. | structure 1 | c. | structure 3 | b. | structure 2 | d. | structure 4 |
|
|
|
5.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cell shown is probably an animal cell
because it
a. | has mitochondria. | c. | has a cell membrane. | b. | does not have a cell wall. | d. | does not have a
nucleus. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Structure 5 is
a. | part of the endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | a
mitochondrion. | b. | a Golgi apparatus. | d. | the nucleus. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Refer to the illustration above. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes are found
in
a. | structure 1. | c. | structure 3. | b. | structure 2. | d. | structure 5. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Structure 2 is
a. | rough endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | a
mitochondrion. | b. | a Golgi apparatus. | d. | the nucleus. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which structure produces vesicles filled with
proteins?
a. | structure 1 | c. | structure 3 | b. | structure 2 | d. | structure 5 |
|
|
|
10.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cell uses structure 3
a. | to transport material from one part of the cell to another. | b. | to package proteins
so they can be stored by the cell. | c. | as a receptor protein. | d. | to produce
ATP. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Refer to the illustration. Structure 1 is
a. | the endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | a
mitochondrion. | b. | a Golgi apparatus. | d. | the nucleus. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The diffusion of water into or out of a cell is called
a. | solubility. | c. | selective transport. | b. | osmosis. | d. | endocytosis. |
|
|
|
13.
|
As a result of diffusion, the concentration of many types of substances
a. | always remains greater inside a membrane. | b. | eventually becomes
balanced on both sides of a membrane. | c. | always remains greater outside of a
membrane. | d. | becomes imbalanced on both sides of a membrane. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The structure labeled A is most likely a
a. | DNA molecule. | c. | chromosome. | b. | signal molecule. | d. | marker protein. |
|
|
|
15.
|
What happens when the structure labeled A binds to the structure labeled
B?
a. | Information is sent into the cell. | c. | The cell begins to undergo
mitosis. | b. | Proteins enter the cell. | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
16.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The structure labeled B in the diagram is an
example of a
a. | channel protein. | c. | receptor protein. | b. | marker protein. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is characteristic of prokaryotes?
a. | They have a nucleus. | b. | Their evolution preceded that of
eukaryotes. | c. | The organelles in their cytoplasm are surrounded by membranes. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
18.
|
Diffusion occurs because
a. | molecules constantly move and collide with each other. | b. | the concentration of
a solution is never the same throughout a solution. | c. | the concentration of a solution is always the
same throughout a solution. | d. | molecules never move or collide with each
other. |
|
|
|
19.
|
A structure within a eukaryotic cell that performs a specific function is called
a(n)
a. | organelle. | c. | tissue. | b. | organ tissue. | d. | biocenter. |
|
|
|
20.
|
A cell will swell when it is placed in a(n)
a. | hypotonic solution. | c. | isotonic solution. | b. | hypertonic solution. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
21.
|
Eukaryotes usually contain
a. | a nucleus. | b. | specialized organelles. | c. | genetic
material. | d. | all of the above. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The main function of the cell wall is to
a. | support and protect the cell. | b. | store DNA. | c. | direct the
activities of the cell. | d. | help the cell
move. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Elongated proteins on the surface of a cell and that identify the cell are
called
a. | marker proteins. | c. | receptor proteins. | b. | channel proteins. | d. | enzymes. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The cell membrane
a. | encloses the contents of a cell. | b. | allows materials to enter and leave the
cell. | c. | is selectively permeable. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
25.
|
The organelles associated with plant photosynthesis are the
a. | mitochondria. | c. | Golgi apparatus. | b. | chloroplasts. | d. | vacuoles. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following does not require energy?
a. | diffusion | c. | active transport | b. | endocytosis | d. | sodium-potassium
pump |
|
|
|
27.
|
Water enters a cell when the solution surrounding the cell is
a. | concentrated. | c. | weak. | b. | hypotonic to the cell. | d. | hypertonic to the
cell. |
|
|
|
28.
|
In a cell, proteins are made on the
a. | mitochondria. | c. | nucleus. | b. | ribosomes. | d. | cell membrane. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which organelle makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the
nucleus?
a. | Golgi apparatus | b. | mitochondrion | c. | vacuole | d. | ribosome |
|
|
|
30.
|
Osmosis is a type of
a. | active transport. | c. | facilitated diffusion. | b. | passive
transport. | d. | endocytosis. |
|
|
|
31.
|
A cell that requires a lot of energy might contain large numbers of
a. | chromosomes. | c. | mitochondria. | b. | vacuoles. | d. | lysosomes. |
|
|
|
32.
|
When a signal molecule binds to a receptor protein, the receptor protein
may
a. | change the permeability of the membrane. | b. | cause the formation
of a second messenger molecule. | c. | speed up the chemical reactions in the
cell. | d. | All of the above |
|
|
|
33.
|
A solution that is hypotonic to a cell has
a. | more solutes than the cell. | c. | the same concentration of solutes
as
the cell. | b. | fewer solutes than the cell. | d. | too many
solutes. |
|
|
|
34.
|
A protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response is
called a
a. | receptor. | c. | vesicle. | b. |
ligand. | d. | proton. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Prokaryotes lack
a. | cytoplasm. | b. | a cell membrane. | c. | a
nucleus. | d. | genetic material. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which process is occurring when a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and
releases its contents outside the cell?
a. | endocytosis | c. | exocytosis | b. | phagocytosis | d. | osmosis |
|
|
|
37.
|
One difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that
a. | nucleic acids are found only in prokaryotes. | b. | mitochondria are
found in larger quantities in eukaryotes. | c. | Golgi vesicles are found only in
prokaryotes. | d. | prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which organelles contain enzymes that break down old cell parts?
a. | centrosomes | c. | vacuoles | b. | lysosomes | d. | chloroplasts |
|
|
|
39.
|
Unlike passive transport, active transport
a. | requires energy. | b. | moves substances down their concentration
gradient. | c. | does not involve carrier proteins. | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
40.
|
Most of the food and waste materials that move into and out of a cell pass
through
a. | receptor proteins. | c. | enzymes. | b. | marker proteins. | d. | channel
proteins. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Molecules that are too large to be moved through the membrane can be transported
into the cell by
a. | osmosis. | c. | exocytosis. | b. | endocytosis. | d. | diffusion. |
|
|
|
42.
|
Phospholipids are molecules that
a. | contain phosphate. | b. | have nonpolar “tails” and polar
“heads.” | c. | form the lipid bilayer of the cell
membrane. | d. | All of the above |
|
|
|
43.
|
Proteins that act like selective passageways in the cell membrane are known
as
a. | marker proteins. | c. | receptor proteins. | b. | channel proteins. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which type of molecule forms a lipid bilayer within a cell membrane?
a. | protein | c. | nucleic acid | b. | phospholipid | d. | carbohydrate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
45.
|
Refer to the illustration above. Structure C is a
a. | carbohydrate chain. | c. | fatty acid. | b. | glycerol molecule. | d. | nucleic acid. |
|
|
|
46.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The structure labeled A is composed of
a. | phospholipids. | c. | proteins. | b. | carbohydrates. | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
47.
|
Refer to the illustration above. The structure that acts as a gate to the
cell’s interior is labeled
|
|
|
48.
|
One important organelle that helps maintain homeostasis by moving substances
from one part of the cell to another is the
a. | endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | Golgi apparatus. | b. | mitochondrion. | d. | cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
49.
|
The packaging and distribution center of the cell is the
a. | nucleus. | c. | central vacuole. | b. | Golgi apparatus. | d. | nuclear
envelope. |
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the following is an example of a prokaryotic cell?
a. | amoeba | c. | bacterium | b. | virus | d. | liver cell |
|
|
|
51.
|
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle that
a. | receives proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum. | b. | packages molecules
made in the endoplasmic reticulum. | c. | is involved in the distribution of
proteins. | d. | All of the above |
|
|
|
52.
|
Only eukaryotic cells have
a. | DNA. | c. | ribosomes. | b. | membrane-bound organelles. | d. | cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
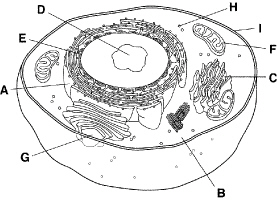
Figure
7-1
|
|
|
53.
|
The structure labeled I in Figure 7-1 is a thin, flexible barrier around a cell.
It is called the
a. | cell membrane. | b. | cell wall. | c. | cell
envelope. | d. | cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
54.
|
Signal molecules bind to
a. | carbohydrates. | c. | receptor proteins. | b. | marker proteins. | d. | transport
proteins. |
|
|
|
55.
|
You probably won't find a cell wall in which of these kinds of
organisms?
a. | plants | b. | animals | c. | fungi | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
56.
|
Which phrase describes the function of the mitochondria?
a. | breaks down chemicals | c. | supplies energy to the cell | b. | packages
proteins | d. | fluid-filled sac
used for storage |
|
|
|
57.
|
Which phrase best describes rough ER?
a. | studded with ribosomes | c. | connected to the Golgi apparatus | b. | protected by
vesicles | d. | stored in the
central vacuole |
|
|
|
58.
|
Plant cells have a large membrane-bound space in which water, waste products,
and nutrients can be stored. This space is called the
a. | mitochondrion. | c. | Golgi apparatus. | b. | chloroplast. | d. | vacuole. |
|