Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1
|
What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous
system?
a) | nerve | b) | neuron | c) | organ | d) | tissue |
|
|
|
2
|
Neurotransmitters are
a) | electrical impulses. | b) | found only in neurons with myelin
sheaths. | c) | released at synapses. | d) | produced by
muscles. |
|
|
|
3
|
Tendons connect
a) | bone to bone. | c) | muscle to muscle. | b) | muscle to bone. | d) | cartilage to
bone. |
|
|
|
4
|
Which type of tissue lines your internal organs?
a) | epithelial | b) | connective | c) | nerve | d) | muscle |
|
|
|
5
|
A group of similar cells that perform a single function is called a(an)
a) | nerve. | b) | organ. | c) | tissue. | d) | organ system. |
|
|
|
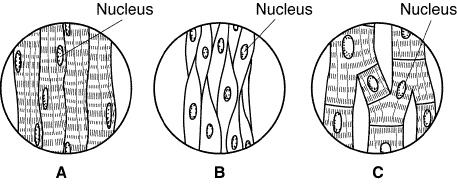
Figure
36-2
|
|
|
6
|
Which diagram(s) in Figure 36-2 show(s) muscles that are striated?
|
|
|
7
|
In Figure 36-2, diagram B is an example of
a) | cardiac muscle. | b) | skeletal muscle. | c) | smooth
muscle. | d) | heart muscle. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8
|
Refer to the illustration above. If neurotransmitters could not be cleared out
of a synapse after transmitting a message,
a) | a postsynaptic neuron would continue to be stimulated for an indefinite period of
time. | b) | the presynaptic neuron could not pass on its impulse. | c) | the postsynaptic
neuron would not be stimulated. | d) | None of the
above |
|
|
|
9
|
Refer to the illustration above. In the diagram, label B indicates a
a) | neurotransmitter molecule. | c) | receptor
protein. | b) | neuromodulator molecule. | d) | drug molecule. |
|
|
|
10
|
Refer to the illustration above. Which labeled object in the diagram would be
responsible for removing neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft?
|
|
|
11
|
Blood, bone, and cartilage are examples of
a) | three different tissue types found in the body. | b) | connective
tissue. | c) | epithelial tissue. | d) | organs of the
body. |
|
|
|
12
|
Defending the body against bacterial infection and invasion by foreign
substances is a function of
a) | red blood cells. | c) | platelets. | b) | plasma. | d) | white blood
cells. |
|
|
|
13
|
Tissue that is specialized to cover the inner and outer surfaces of the internal
organs is called
a) | epithelial tissue. | c) | muscles tissue. | b) | connective tissue. | d) | nerve tissue. |
|
|
|
14
|
Where is cardiac muscle tissue located in the body?
a) | heart | b) | ribs | c) | skull | d) | bones |
|
|
|
15
|
Bone cells that become embedded within the concentric layers of bone tissue
are
a) | osteocytes. | c) | red marrow cells. | b) | periosteal cells. | d) | yellow marrow
cells. |
|
|
|
16
|
Red blood cells
a) | transport respiratory gases. | c) | destroy
viruses. | b) | combat bacterial infection. | d) | transport cholesterol. |
|
|
|
17
|
The three types of muscle tissues are
a) | skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. | c) | smooth, cardiac, and
involuntary. | b) | skeletal, voluntary, and cardiac. | d) | skeletal, cardiac, and
ridged. |
|
|
|
18
|
The thin outer layer of the skin is
a) | the dermis. | c) | the fatty layer. | b) | the epidermis. | d) | connective
skin. |
|
|
|
19
|
Ligaments connect
a) | cartilage to bone. | b) | muscle to muscle. | c) | bone to
muscle. | d) | bone to bone. |
|
|
|
20
|
From the smallest functional units to the largest, the body is organized as
follows:
a) | cell, system, organ, tissue, body. | c) | system, organ, tissue, cell,
body. | b) | organ, cell, tissue, system, body. | d) | cell, tissue, organ, system,
body. |
|
|
|
21
|
Smooth muscles can be found
a) | attached to the skeleton. | c) | at the knee
joint. | b) | in the wrist bones. | d) | in internal organs. |
|
|
|
22
|
Tightly connected cells that are arranged in flat sheets are characteristic
of
a) | epithelial tissue. | c) | muscle tissue. | b) | connective tissue. | d) | nerve tissue. |
|
|
|
23
|
Organs that work together form
a) | connective tissues. | c) | organ systems. | b) | tissue systems. | d) | All of the
above |
|
|
|
24
|
Hormones are essential to maintaining homeostasis mainly because
a) | they catalyze specific chemical reactions in brain cells. | b) | the body requires
them for digesting food. | c) | they cause specific responses in specific
cells. | d) | they act faster than nerve impulses. |
|
|
|
25
|
The heart and the blood vessels are separate organs that form the
a) | skeletal system. | c) | reproductive system. | b) | circulatory system. | d) | digestive
system. |
|
|
|
26
|
The four basic types of tissue in the human body are
a) | cell, organ, and organ system. | b) | sight, smell, and hearing. | c) | thyroid, trachea,
adenoid, and bronchus. | d) | muscle, nervous, connective, and
epithelial. |
|
|
|
27
|
Which system regulates and controls the body’s functions?
a) | endocrine system | b) | lymphatic system | c) | integumentary
system | d) | skeletal system |
|
|
|
28
|
The levels of organization in the body include
a) | endocrine, respiratory, digestive, and nervous. | b) | cells, tissues,
organs, and organ systems. | c) | cells, tissues, and organs. | d) | lymphatic,
respiratory, and circulatory. |
|
|
|
29
|
The process by which organ systems maintain a controlled, stable, internal
environment is called
a) | circulation. | b) | organization. | c) | homeostasis. | d) | teamwork. |
|
|
|
30
|
What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in its
environment?
a) | a threshold | b) | an action potential | c) | an
impulse | d) | a dendrite |
|
|
|
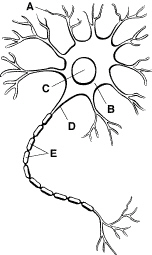
Figure
35-1
|
|
|
31
|
Refer to Figure 35-1. The cell body of a neuron collects information from which
structure?
|
|
|
32
|
Which body system acts as a transportation system?
a) | circulatory | b) | respiratory | c) | nervous | d) | excretory |
|
|
|
33
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of the circulatory system?
a) | heart | b) | air passageway | c) | series of blood
vessels | d) | blood |
|
|
|
34
|
Which of the following blood cells contain hemoglobin?
a) | red blood cells | b) | white blood cells | c) | platelets | d) | all of the
above |
|
|
|
35
|
The function of the urinary system is to
a) | break down nutrients. | b) | remove wastes. | c) | absorb
nutrients. | d) | prevent infection. |
|
|
|
36
|
The main organs of the urinary system are the
a) | kidneys. | b) | lungs. | c) | intestines. | d) | ureters. |
|
|
|
37
|
The endocrine system
a) | affects only the reproductive system. | b) | releases hormones into the
bloodstream. | c) | competes with the nervous system. | d) | is made up primarily of glands with
ducts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
38
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cells shown in the diagram are
a) | filled with plasma. | c) | red blood cells. | b) | platelets. | d) | white blood
cells. |
|
|
|
39
|
Refer to the illustration above. The cells shown in the diagram
a) | can live for at least a year. | b) | are the largest cells in the circulatory
system. | c) | promote clotting. | d) | contain
hemoglobin. |
|
|
|
40
|
Tendons connect
a) | bone to bone. | c) | muscle to muscle. | b) | muscle to bone. | d) | cartilage to
bone. |
|
|
|
41
|
A muscle can
a) | push a bone. | b) | pull a bone. | c) | both push and pull a
bone simultaneously. | d) | sometimes push and sometimes pull a
bone. |
|